Flexible robotic arms are a new type of bionic robotic arm designed after certain living organisms including earthworms, snakes, elephant trunks, and octopus tentacles. Unlike traditional robotic arms, flexible robotic arms can bend in any orientation within the boundaries of material deformation and can adapt to small and complex spaces.
Flexible robotic arms have seen applications in various fields including surgery, space missions, and equipment maintenance. These situations often have very high accuracy requirements. Most of the research in the field is focused on improving the reliability of the arm’s movement and decreasing the error while tracking the arm’s trajectory, as a dynamic model for flexible robotic arms is difficult to design.
Researchers from the Sichuan University School of Electrical Engineering deigned a flexible coupling rod-driven robotic arm. Through the analysis of the movement mechanisms, the researchers also developed an end positioning control algorithm based on the inverse dynamic model, then conducted various end positioning control experiments both through simulation and with a physical prototype.
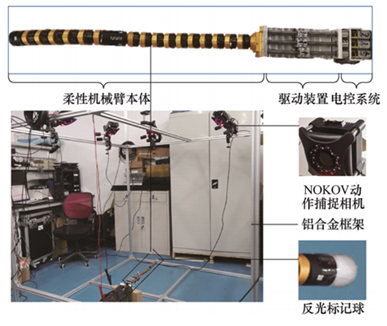
The physical prototype of the flexible robotic arm is composed of the flexible arm itself, a driving device, and an electronic control system, in which the control system sends instructions to the driving device, which actuates a driving rod to regulate the robot’s movement. To accurately record the movement and positioning of the end of the robotic arm, the researchers arranged a NOKOV optical motion capture system above the robotic arm body and placed a reflective marker at the end of the flexible arm. The NOKOV motion capture system used throughout the experiment achieved sub-millimeter accuracy in its measurements.
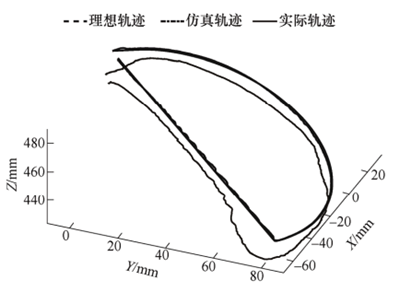
The researchers compared the ideal trajectory with the simulated trajectory and the actual trajectory obtained by the NOKOV motion capture system and analyzed the errors of the physical prototype. The experiment shows the efficacy of the end positioning control algorithm based on the inverse dynamic model.
Bibliography: