Harvesting robots play an important role while harvesting fruit, allowing for shorter picking times, reduced picking costs, reduced manual labor, and can drastically improve fruit agriculture.
Currently, harvesting robots are unable to differentiate between stages of fruit growth and have difficulty detecting obstructed fruits. This may cause the fruit to be improperly picked or damage the picking arm. Yang Changhui of the Chongqing University of Technology lead a team that studied the classification, identification, and localization methods of ripe citrus fruits in various natural environments to develop a model to help detect and harvest ripe fruit autonomously.
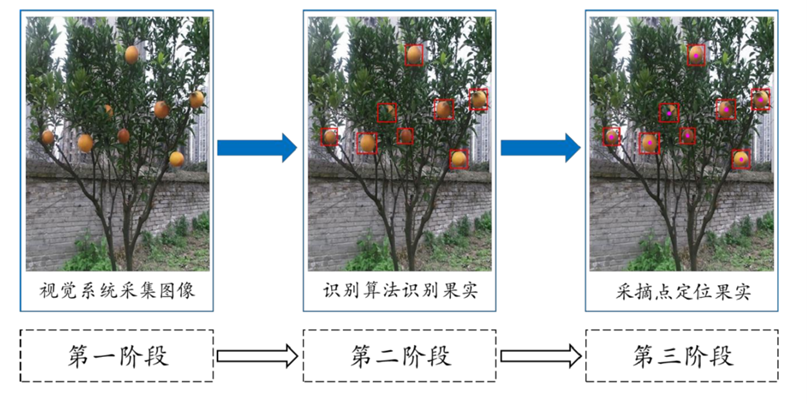
To develop an accurate and reliable fruit identification and positioning system, the research team used the NOKOV motion capture system. Testing was conducted in a laboratory environment and attempted to test the positioning accuracy of the fruit in any position.
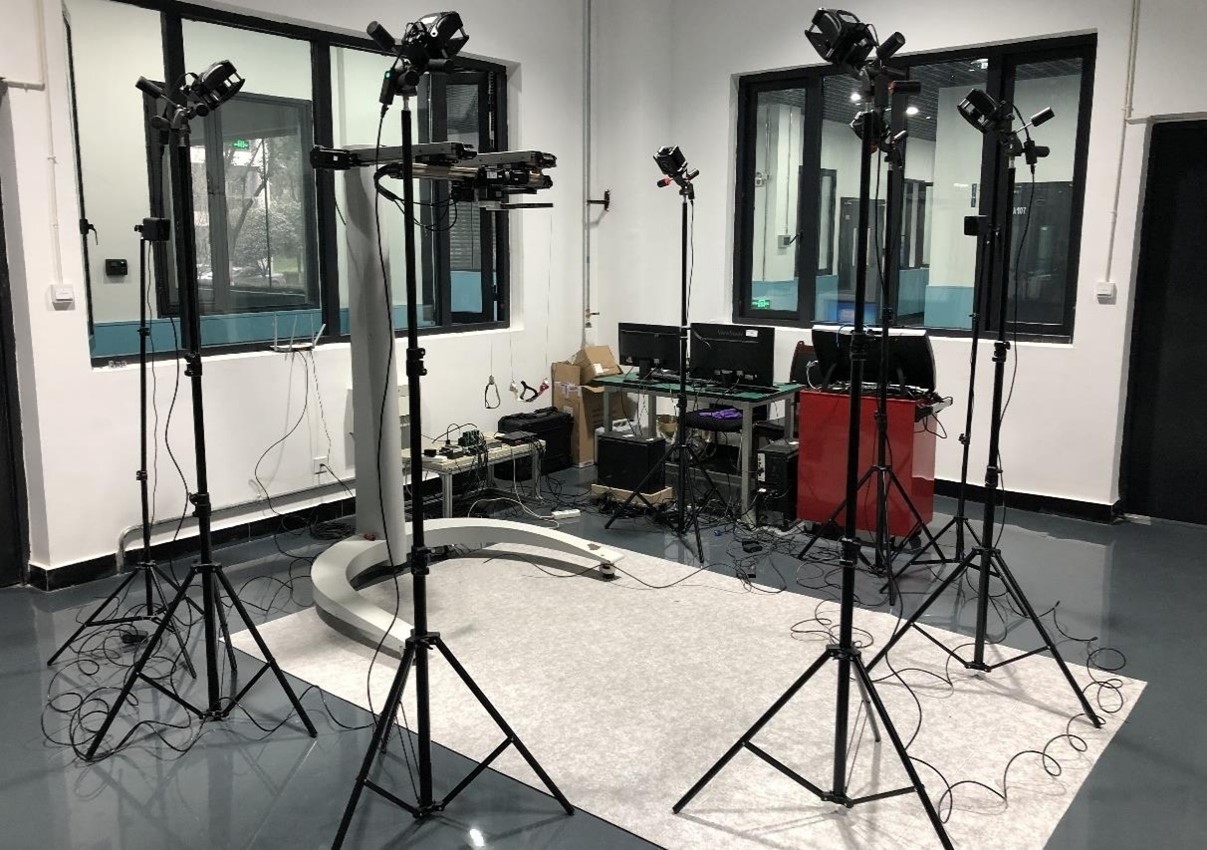

The experimental process is shown in the following figure: a Kinect camera was fixed to a liftable bracket while a citrus fruit was hung anywhere within the range of the camera system. The position of the fruit is captured by the NOKOV motion capture system while an estimated position calculated by the positioning system developed by the team. The accuracy of the positioning system was evaluated by comparing the two results.
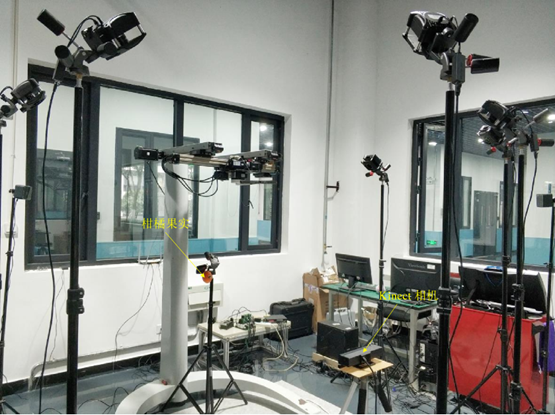

Comparing the positions of 20 sets of citrus fruits in different orientations as measured by the NOKOV motion capture system and calculated by the Kinect positioning system, the average positioning error in the x-direction is 2.51mm, while the average error in the y-direction is 2.71mm and the average error in the z-direction is 3.35mm. From these experimental results, the researchers concluded that the errors accumulated fall within the bounds of experimental error and that the Kinect positioning system meets the accuracy requirements to reliably pick fruit.
Bibliography: