Applied Energy | Dynamic behavior and energy flow of floating triboelectric nanogenerators
Prof. Wang Zhonglin's team from the Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences, published a paper titled "Dynamic behavior and energy flow of floating triboelectric nanogenerators" in the journal of Applied Energy, which is indexed by SCI&EI.
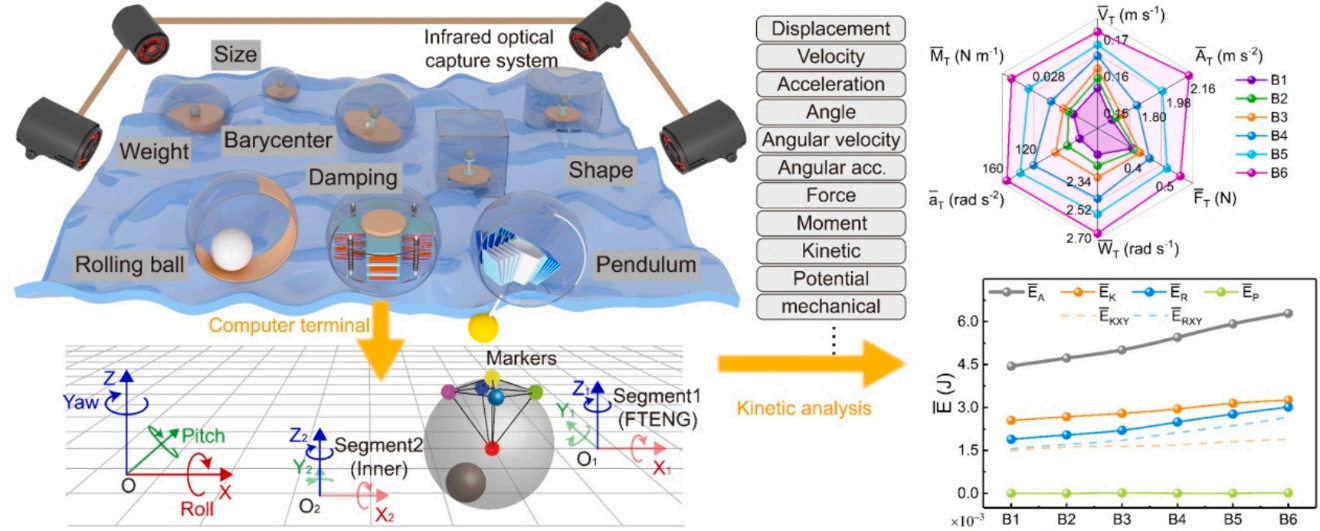
The authors used the NOKOV Motion Capture System to obtain the six degrees of freedom (6DoF) information of different floating triboelectric nanogenerators (F-TENGs) under the excitation of water waves for the first time. Based on statistical data from 118 research papers, the most universally applicable modes/parameters and non-rigid body models were systematically explored. The six-dimensional kinematic radar matrices and energy gradient curves peeled from the calculation and statistics of the 6DoF data comprehensively reveal the dynamic behavior and energy flow characteristics of F-TENGs when interacting with water waves. The research results can serve as an enlightening framework for structural design, optimizing the utilization of F-TENGs for blue energy.
Citation
Shuxing Xu, Jiabin Zhang, Erming Su, Chengyu Li, Wei Tang, Guanlin Liu, Leo N.Y. Cao, Zhong Lin Wang, Dynamic behavior and energy flow of floating triboelectric nanogenerators, Applied Energy, Volume 367,2024,123468,ISSN0306-2619, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123468.
Research Background
Wave energy is a vast and ubiquitous clean energy source that has always been a hot topic in the field of new energy harvesting. Among these studies, floating triboelectric nanogenerators (F-TENGs) that harness energy through frictional and electrostatic induction processeshave garnered significant acclaim, owing to their high degree of coupling with the operational cycles of sea breeze and ocean waves , lightweight construction facilitating effortless buoyancy, low manufacturing costs, and scalability for large-scale deployment. However, there are still challenges, including impractical coupling methods between waves and F-TENGs, a lack of systematic dynamic detection and analysis methods, and a tendency toward excessive parameter optimization. On the other hand, the dynamic study of F-TENGs is one-sided and lacks systematic research on the dynamic variations of different or universal F-TENGs. Therefore, comprehensively and systematically understanding the dynamic behavior and energy flow characteristics of F-TENGs when interacting with water waves becomes the focus of this paper.
Research Highlights
1. A novel method is introduced for the sixdegree-of-freedom analysis of floating triboelectric nanogenerators (F-TENGs).
2. The non-rigid models with control variables are universal and close to the real situation.
3. F-TENGs’ comprehensive attitude tracking and analysis of dynamics/energy under wave excitation are provided.
4. The resulting rules can facilitate and guide the structural optimization of F-TENGs for wave-energy conversion.
5. Fluid dynamics analysis software is employed to elucidate the rules governing F-TENG parameters.
Experiment
The experiment was conducted in an indoor rectangular pool measuring 1.2 meters × 1.0 meters × 1.0 meters with a water depth of 0.6 meters, equipped with a wave generator rated at 50w, and NOKOV Motion Capture System was used to track the motion of F-TENGs.
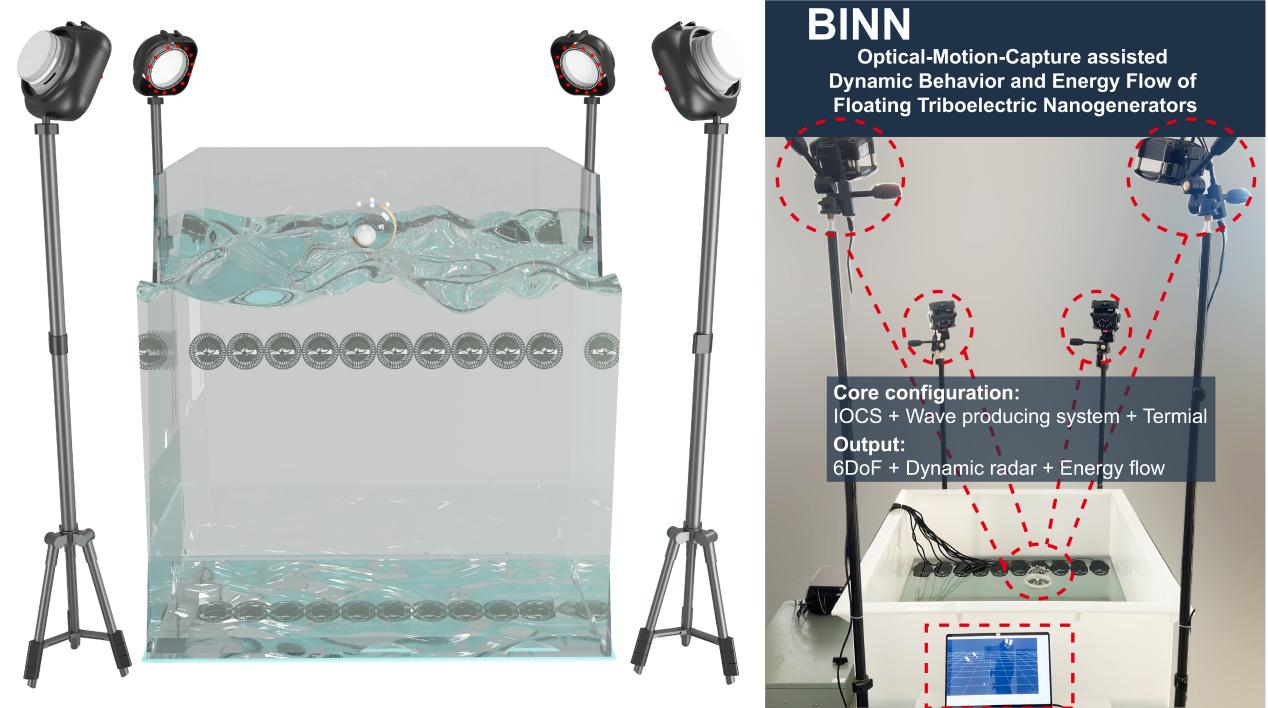

Figure 1 - Test environment in a real pool
By analyzing various indicators of different floats, including center of gravity, weight, diameter, size, and basic modes, including rolling mode, elastic mode, and assist mode, a comprehensive posture tracking and dynamic/energy analysis of F-TENGs under water wave excitation were provided.
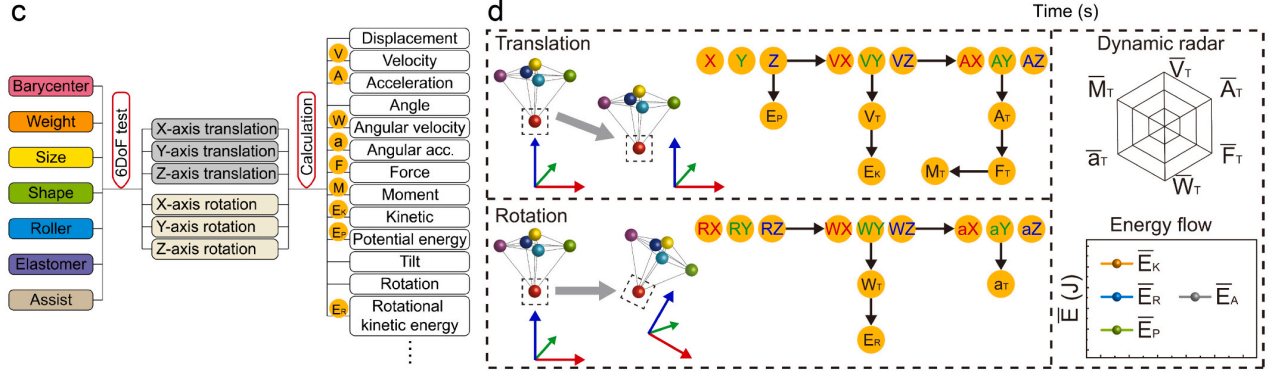
Figure 2 - c) Overall flowchart of dynamic calculations d)Flowchart of dynamic calculation process
Through dynamic calculations, including differentiation, vector synthesis, parameter substitution, and 6DoF statistics, the dynamic data of F-TENGs, such as velocity, acceleration, force, angular velocity, angular acceleration, and moment, were analyzed and simulated to assist in analyzing the response of F-TENGs under wave excitation.
These standardized tests and models of universal modes and basic parameters can effectively assist in the future structural design and optimization of F-TENGs. In addition, this visually integrated testing method provides an effective approach for trajectory tracking, multi-dimensional analysis, multi-body motion observation, and simulation validation of F-TENGs.
NOKOV Motion Capture System provides high-precision pose data for floating triboelectric nanogenerators (F-TENGs), aiding in comprehensive posture tracking and dynamic/energy analysis between F-TENGs and water waves.
Author Introduction
Xu Shuxing, Ph.D. candidate at the Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, blue energy, self-powered sensing.
Zhang Jiabin, Ph.D. candidate at the University of Science and Technology of China, School of Biomedical Engineering. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, self-powered sensing, intelligent logistics.
Su Erming, Ph.D. candidate at the Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, blue energy, high-precision 3D printing.
Li Chengyu, Postdoctoral fellow at the Smart Wearable Systems Research Institute, Hong Kong Polytechnic University. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, wearable devices, motion monitoring.
Tang Wei, Researcher and Ph.D. supervisor at the Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, self-powered sensing, contact electrocatalysis.
Liu Guanlin (Corresponding Author), Associate Professor at the Nanocenter, Guangxi University. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, blue energy.
Cao Nanyin (Corresponding Author), Associate Researcher at the Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Research Interests: triboelectric nanogenerators, blue energy, 3D printing technology.
Wang Zhonglin (Corresponding Author), Institute of Nanoenergy and Nanosystems, Chinese Academy of Sciences and Georgia Institute of Technology, Professor and Academician