Surgical assistant robot has the characteristics of accurate control, stable operation and high operation precision, which can help surgeons overcome the difficulties in operation precision, working space, distance and cooperative work of traditional surgery.
In order to make the surgical robot system realize the high quality automatic operation like the doctor, an important basic work is to establish the surgical operation model. To this end, Professor Yang Dewei's team from Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications took superficial tissue suturing as the modeling object to study suturing skills and modeling.
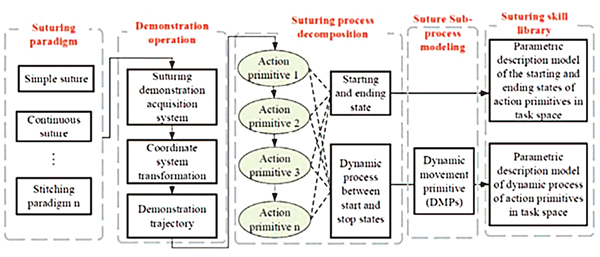
In order to solve the problem of poor migration ability of traditional models in new scenarios, Professor Yang proposed a "demonstration-disintegration-modeling" skill learning modeling framework. The suture process was decomposed into several sub-processes, and DMPs method was used to model the trajectories of the sub-processes.
The method of learning from demonstration has better migration ability for scenes with similar but different trajectories. In order to obtain the data during the suture demonstration, the researchers established a suture demonstration acquisition system.
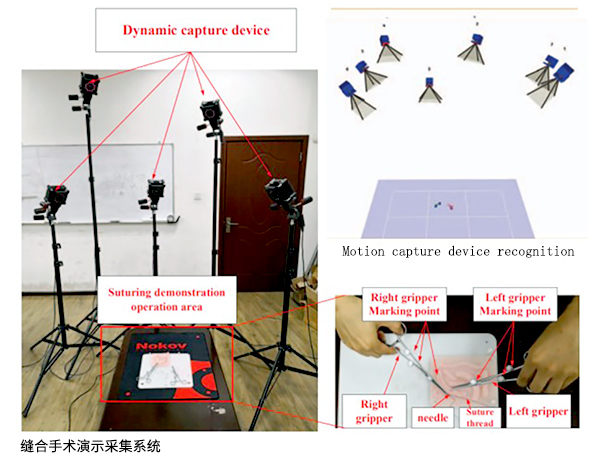
The system includes NOKOV motion capture system, needle holder, suture needles, thread and wound model. The NOKOV motion capture system is equipped with 7 infrared optical cameras to measure and capture the stitching process. Two needle holders are respectively pasted with 3 markers. The motion capture system was used to obtain the three-dimensional coordinates of the markers, and the continuous real-time position and posture trajectory of the needle holder were calculated.
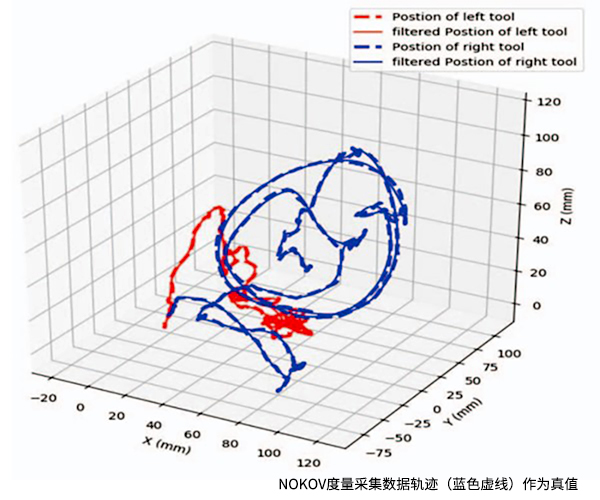
As shown in the figure below, the motion trajectory of the needle holders in the wound coordinate system can be obtained through coordinate transformation. In order to eliminate the doctor's hand shaking, the track data is processed by low-pass filter.
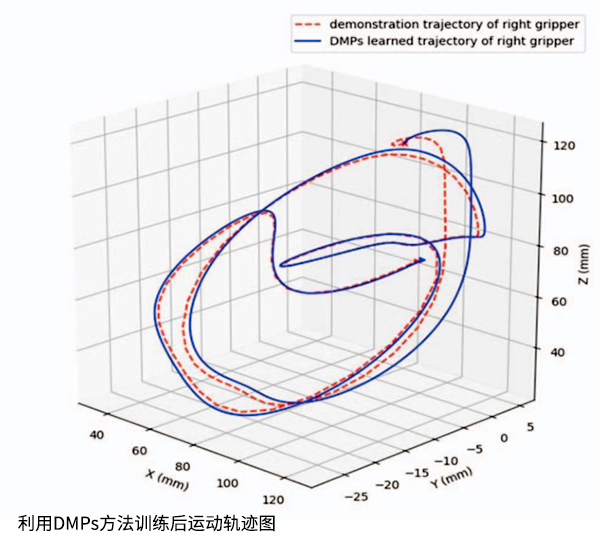
The suturing process can be divided into 3 stages: needle penetration into skin tissue, tie a knot, and then tighten the sutures. The DMPs method proposed by the author can represent the dynamic process at each stage. The figure below shows the trajectories obtained after training using DMPs method. It can be seen that the trajectory obtained by DMPs is in good consistency with the real trajectory.
One advantage of DMPs model is good migration effect. As shown in the figure below, the dynamic process of suture is similar when the endpoint position is changed, which makes it easy to use the learning suture model to plan new trajectories for various positions and types of wounds.
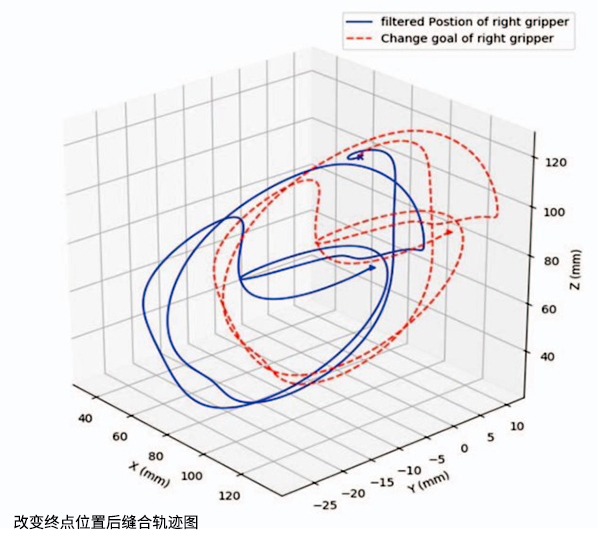
Solid blue lines: Suture tracks collected by NOKOV's motion capture system
Red dotted line: Corresponding track after DMPs learning after changing target position
References:
[1] D. Yang, Q. Lv, G. Liao, K. Zheng, J. Luo and B. Wei,"Learning from Demonstration: Dynamical Movement Primitives Based Reusable Suturing Skill Modelling Method," 2018 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC),2018, pp. 4252-4257, doi: 10.1109/CAC.2018.8623781.