For optical motion capture equipment, its core product—the optical motion capture camera—comes in various specifications. This article will introduce two important parameters that affect the performance of optical motion capture equipment: resolution and frequency.
Resolution:
Reflected markers captured in the camera's view are presented as pixels, with each marker's center point extracted as a pixel image to obtain its two-dimensional coordinates. The more circular the shape of a point in the camera's view, the more accurately its extracted center coordinate will be.
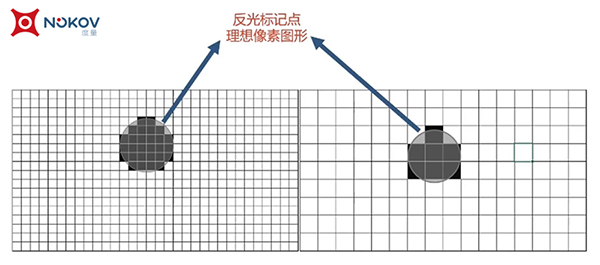
As shown in the figure, the high-resolution camera captures reflective markers with a greater number of pixels, making the pixel shape more circular compared to the low-resolution camera, thus allowing for more precise extraction of the center points of the pixel shapes.
Therefore, compared to a camera with a resolution of 1.3 megapixels, a camera with a resolution of 12 megapixels will capture data with higher precision under other equal conditions.
Frequency:
Camera frequency, also known as frame rate, is the number of frames per second a camera outputs, denoted as fps (frames per second) or in Hertz (Hz), with 300Hz meaning 300fps.
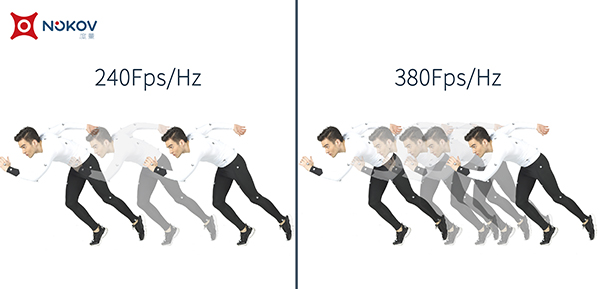
In the process of using optical motion capture equipment, the camera performs high-speed image capture. For optical motion capture devices, a higher camera frequency results in more image data collected in the same timeframe, allowing for more accurate restoration of the captured object's motion trajectory. Consequently, the precision of the 3D spatial data obtained through computation increases.