The new robotic system that assists minimally invasive surgery in the thymic cavity acts as the "third hand" of the surgeon, which is used to replace the assistant to hold the endoscope and pull tissues, and can assist the surgeon to complete the operation independently. Flexible surgical instruments have a high degree of freedom and can flexibly adjust their poses, making them ideal for performing surgical tasks in confined work spaces. However, redundant degrees of freedom will increase the difficulty of its kinematics solution.
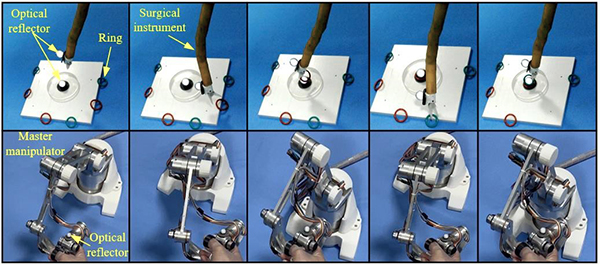
From the perspective of force balance, the team of Feng Mei from the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering of Jilin University proposed a structure of a flexible surgical instrument with constant curvature, which can quickly and accurately respond to commands and meet the master-slave control requirements of real-time surgery. In order to verify the performance of the flexible surgical instrument under fine manipulation, the researchers conducted a prototype experimental verification. In the experiment, the doctor's main hand controlled the instrument to grab the ring at the target position, as shown in the figure.
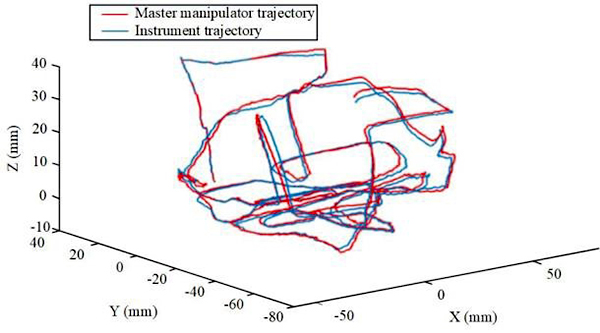
The research team used the NOKOV motion capture system to obtain the motion trajectory information of the master hand (controlled by the doctor) and the slave surgical instruments in real time as the experimental results, and fixed the reflective markers on the master hand and the end effector of the instrument respectively.
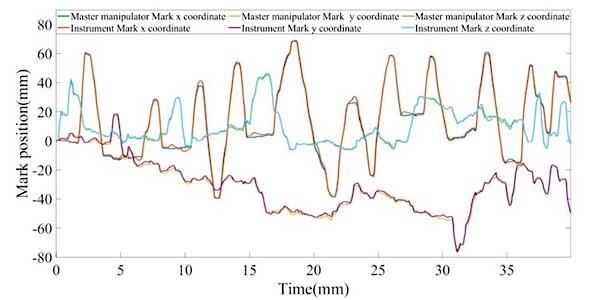
The positional motion trajectories of the master hand and the instrument along the x, y and z directions, respectively. The experiments yielded RMSEs of 0.498, 0.399, and 0.051 for the expected and actual trajectories of the flexible surgical instrument in the x, y, and z directions, respectively. It is proved that the surgical instrument mechanism can perform fine operation well under the master-slave operation.
The kinematic solution method proposed by the research team is not limited by the mechanical structure, and it can be applied to any flexible device with constant curvature bending. At the same time, the flexible surgical instrument effectively improves the precision and flexibility of the surgical operation. The research paper was published by ICRA 2021.
Bibliography:
[1] Feng,M., Ni, Z.X., Li, A., Lu, X. and Fu, Y.L. (2021), Master manipulatoroptimisation for robot assisted minimally invasive surgery. Int J Med Robot,17: e2208. https://doi.org/10.1002/rcs.2208.