Most of the current industrial welding is done by industrial robots. In the field of arc welding, the traditional welding workstation composed of welding robots, positioners, and fixtures can no longer meet the current needs for small batches and customized flexible automated production. The collaborative welding system composed of multiple robots has stronger operation capacity, wider working space, more flexible system structure and organization, which can overcome the shortcomings of traditional welding workstations.
For a typical multi-robot welding system with two handling robots and one welding robot, controlling the cooperative motion of the two handling robots is the key to achieve high-quality welding. The problems to be solved include: the trajectory planning of the two-robot cooperation, the modeling of the two-robot cooperation system, and the position/force coordination control of the two-robot cooperation.
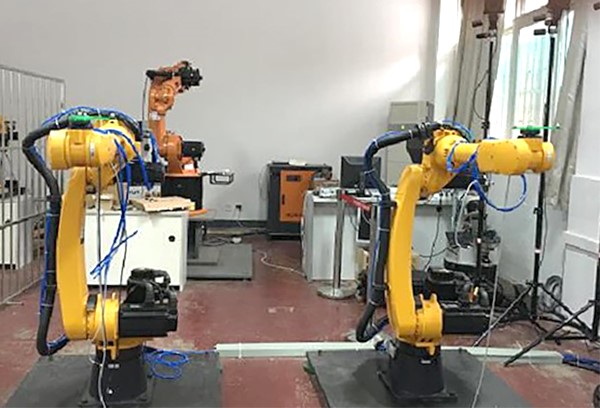
Researchers from the School of Automation of Southeast University have carried out research on the subject of peer-to-peer cooperative control of two robots. The object-oriented trajectory planning is used in the research, and a simulation platform is built for verification. At the same time, mathematical modeling is carried out for the dual robots, the end mapping relationship is determined, and the position-based impedance control is used to adjust the position/force relationship in the cooperative process of the dual robots.
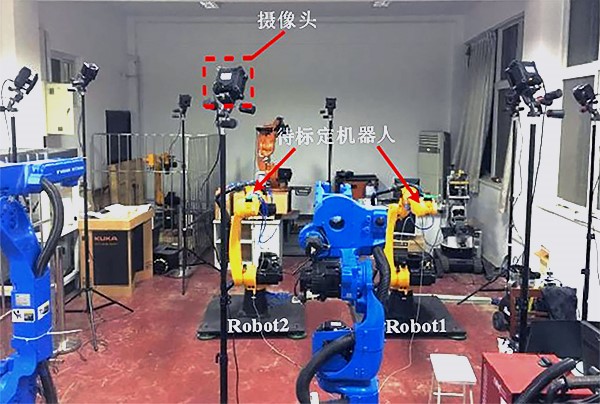

In order to test the effectiveness of the verification system, the researchers took two Estun ER16 robots as control objects, and completed the splicing motion of the two-robot cooperative clamping of steel pipes. For the planning of the motion trajectory of the dual-robot cooperative system, it is first necessary to determine the relative pose of the base coordinate system of the dual-robot. In the experiment, a customized workpiece for calibration was installed at the ends of the two robots, and 3 markers were installed on each calibration workpiece. And the distance from the marker on the center of the circle to the center of the other two markers is 100mm. The NOKOV optical three-dimensional motion capture system is used to locate the markers on the two sets of workpieces, so that the pose of the workpiece at the end of the robot can be determined, and then the relative position and posture of the two robots can be measured.
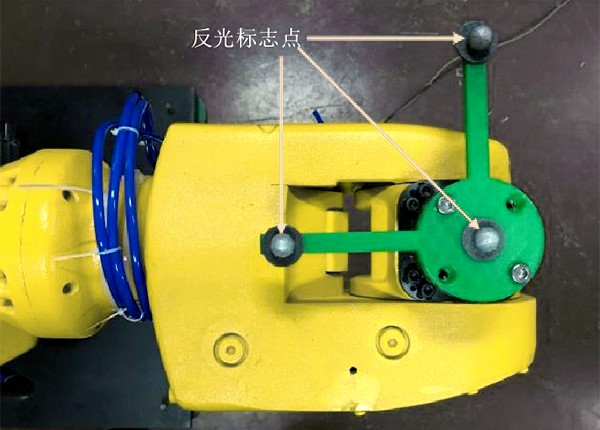
The positioning accuracy of the NOKOV optical motion capture system reaches sub-millimeter level, and it can accurately obtain real-time 6DoF of the target, ensuring the smooth progress of scientific research projects.
Bibliography:
[1]Research on peer-to-peer cooperative control of dual robots based on impedance model[D]. CHEN Ming. Southeast University, 2018.