Assistant Professor Gao Yixing from the School of Artificial Intelligence at Jilin University presented new advances in robot-assisted dressing and garment grasping at ICRA 2023, a top-tier international conference in robotics. The study utilized the NOKOV motion capture system to provide real-time position and posture data of garment grasping points.
Research Achievement 1: Clothes Grasping and Unfolding Based on RGB-D Semantic Segmentation
In the field of intelligent robotics for elderly care and disability assistance, robot-assisted dressing presents a profoundly challenging task, where garment grasping and unfolding constitute the crucial and central components. Some studies primarily train recognition models for graspable points using single-input multi-noise depth images, while leveraging synthetic data to reduce annotation costs. However, noise interference and feature distribution discrepancies between synthetic and real domains often lead to performance degradation. Additionally, approaches based on predicting point coordinates tend to fail due to deformation and occlusion of flexible objects like clothing.
Thus, Gao Yixing team proposed an RGB-D semantic segmentation model (Bi-directional Fractal Cross Fusion Network, BiFCNet) to identify regions rich in semantic information, enabling robots to predict and estimate graspable areas on target garments. To reduce the high data annotation costs associated with model training, the team also introduced a multi-input data augmentation method based on adversarial strategy. Finally, the entire system and the task pipeline for grasping and unfolding were designed based on a graspable point selection approach that incorporates grasping direction considerations.
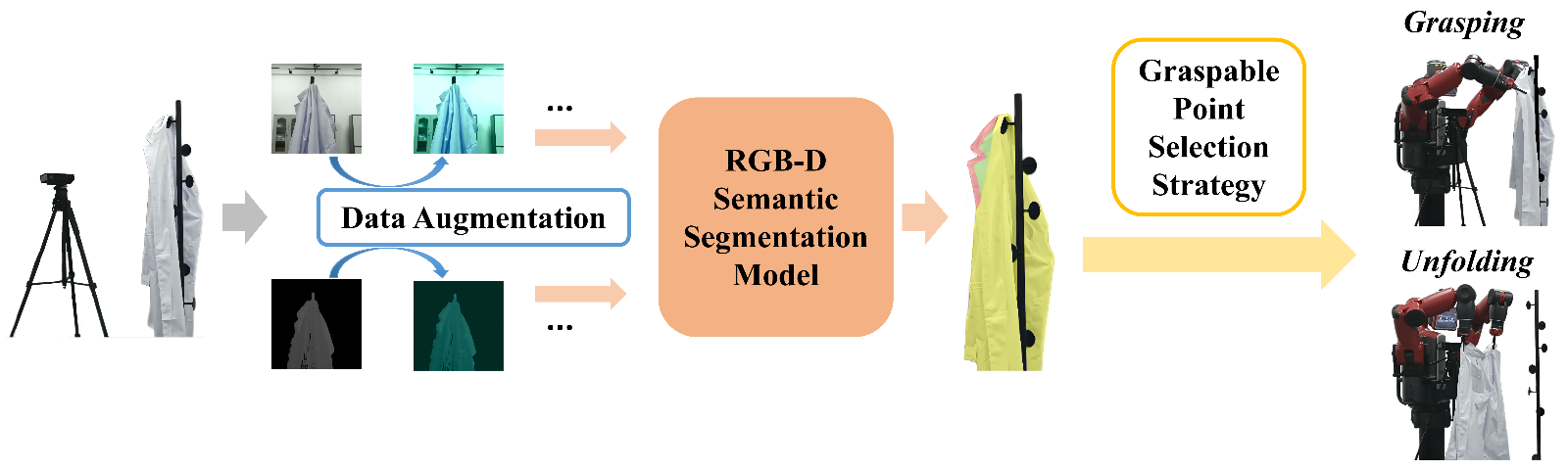
Clothes Grasping and Unfolding Pipeline Based on Data Augmentation, RGB-D Semantic Segmentation, and Graspable Point Selection Strategy
Regarding the proposed RGB-D semantic segmentation model BiFCNet, the entire network adopts an encoder-decoder architecture. The encoder consists of two parallel ResNet-101 networks serving as the backbone feature extraction networks. The outputs from each layer of ResNet-101 are fused in the Fractal Cross Fusion (FCF) module. Within the FCF feature fusion module, two distinct feature processing paths are established: channel weight extraction and cross-fusion propagation. The Fractal Process (FP) module within the cross-fusion propagation path can extract global complex features based on fractal geometry. The two paths ultimately converge to produce fused feature maps. DeepLab V3+ is employed as the feature decoder, with fusion results from the first and last FCF modules used as shallow and deep feature inputs to the DeepLab V3+ network respectively. Finally, the decoder performs feature decoding to output the segmentation map.
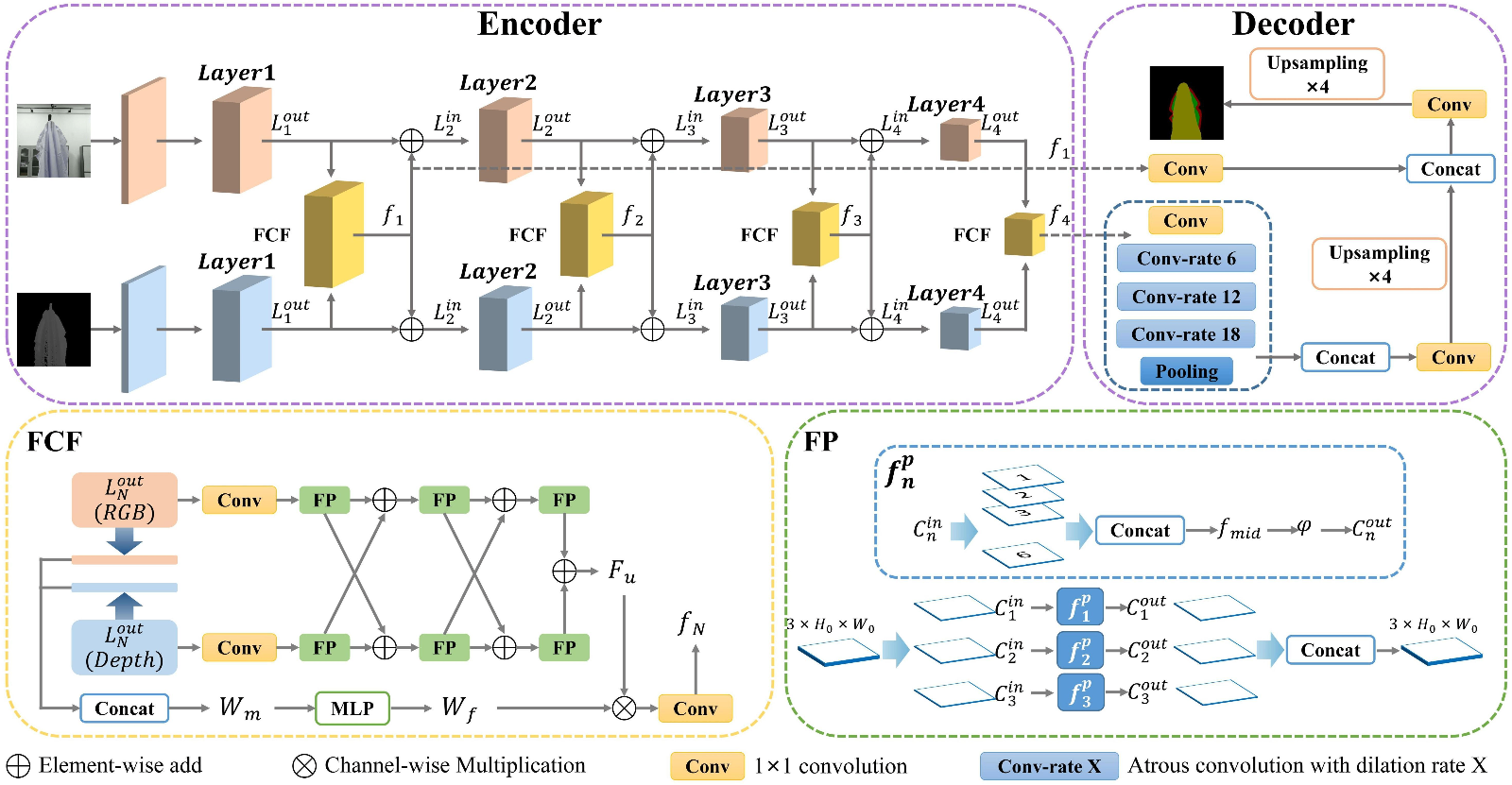
the RGB-D semantic segmentation network (Bi-directional Fractal Cross Fusion Network, BiFCNet)
The aforementioned research has been accepted for presentation at the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), under the title "Clothes Grasping and Unfolding Based on RGB-D Semantic Segmentation".Source:https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2305.03259
Research Achievement 2: Cross-Domain Representation Learning for Clothes Unfolding in Robot-Assisted Dressing
Regarding robot-assisted dressing, existing research has primarily focused on the dressing process itself, under the assumption that the garment has already been grasped by the robot. However, prior to performing assisted dressing, the robot must first unfold the garment into a wearable state.
In the study of robotic garment unfolding, accurately identifying grasping points on clothing is one of the most critical steps. With the advent of deep learning, researchers have begun using convolutional neural networks to learn the Cartesian coordinates of grasping points from large-scale labeled data. However, collecting real-world data with annotated information is highly time-consuming and labor-intensive. Consequently, using physics engines to generate synthetic images for augmenting training datasets has become a widely adopted paradigm in robotic garment unfolding research.
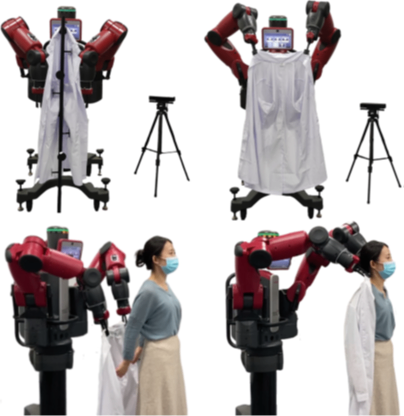

The Baxter humanoid robot autonomously identifies grasping points on a hanging garment, unfolds it to a wearable state, and assists the user in dressing.
To address the inherent domain gap between real and synthetic images, the team proposed a Cross-Domain Representation Learning (CDRL) network capable of effectively distilling knowledge from both synthetic and real domains to generate more robust cross-domain feature representations. The CDRL network primarily consists of two modules: the Domain-Specific Feature Refinement (DSFR) module extracts domain-invariant image features, which are then adaptively refined through two domain-aware deformable convolutional branches to generate domain-specific knowledge.The Cross-Domain Feature Representation Fusion module obtains cross-domain representations by fusing features from the two domain-specific branches, thereby integrating domain-specific knowledge and enhancing recognition accuracy of the model.
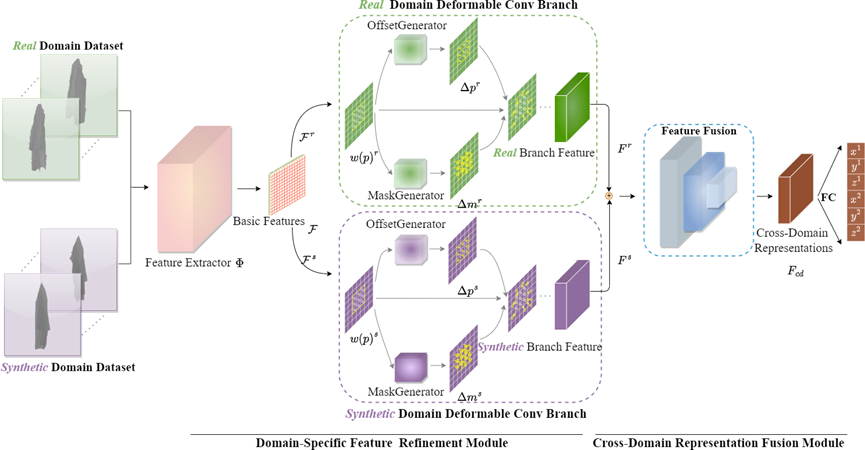
Cross-Domain Representation Learning (CDRL)
Regarding implementation details, Gao Yixing and her team leveraged the Maya physics engine to generate large-scale synthetic garment images with grasp point annotations, while utilizing the NOKOV motion capture system to acquire real-depth images annotated with garment grasping points. Compared with five baseline methods, the CDRL approach achieved superior performance in garment grasp point identification and further reduced recognition errors. When deployed on the Baxter robot, the system successfully assisted six participants with dressing by first unfolding the garments and then recognizing the real-time joint positions of the users to complete the dressing assistance.
This research achievement, entitled "Cross-Domain Representation Learning for Clothes Unfolding in Robot-Assisted Dressing," has been accepted for presentation at the 2022 ECCV Workshop on Assistive Computer Vision and Robotics.Source:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25075-0_44
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The Humanoid Robotics and Vision team at Jilin University, led by Professor Gao Yixing, has provided novel approaches for robotic garment grasping, unfolding, and robot-assisted dressing. As robot path planning methodologies continue to advance, coupled with improvements in model recognition accuracy and motion capture performance, we can anticipate more sophisticated robot-assisted dressing solutions. Looking ahead, with the full commercial implementation of technological achievements, we will witness humanoid robots unlocking substantial market potential across various fields including smart healthcare, elderly and disability assistance, home services, and scientific research.
About Gao Yixing

Gao Yixing: Ph.D. She is an Associate Professor and Doctoral Supervisor at the School of Artificial Intelligence, Jilin University, a High-Level Talent of Jilin Province, and leads the Humanoid Robotics and Vision Laboratory.
She has long been engaged in research focusing on humanoid robots, computer vision, robotic vision, and human-computer interaction. She has published more than 10 high-level papers as first author or corresponding author in top international conferences and journals in the fields of robotics, computer vision, and artificial intelligence (such as CVPR, ICCV, ICRA, IROS, KBS, etc.). She also serves as a reviewer for flagship journals and conferences in robotics, computer vision, and artificial intelligence. As the project leader, she is presiding over the National Natural Science Foundation of China Youth Program "Research on Optimization Methods for Robot Grasping and Transferring Target Positions with Visual Cooperative Perception" (2023-2025).She was admitted to the Special Class for the Gifted Young of Xian Jiaotong University at the age of 15, where she completed her combined bachelor and master program, and was recommended for admission to the Automation major of the School of Electronic and Information Engineering at Xian Jiaotong University. She received a full doctoral scholarship under the National Study Abroad Fund International Graduate Program and earned her Ph.D. from Imperial College London under the supervision of Professor Yiannis Demiris, Fellow of the Royal Academy of Engineering. She subsequently conducted postdoctoral research at Imperial College London and served as a Teaching Fellow in the School of Computer Science at the University of Birmingham, where she taught three courses: Intelligent Robotics, Computer Vision and Imaging/Robot Vision, and Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning.
Personal Homepage: https://sai.jlu.edu.cn/info/1094/3451.htm