A research team from the School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University, has published a paper titled "A deep learning-enabled visual-inertial fusion method for human pose estimation in occluded human-robot collaborative assembly scenarios" in Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing.
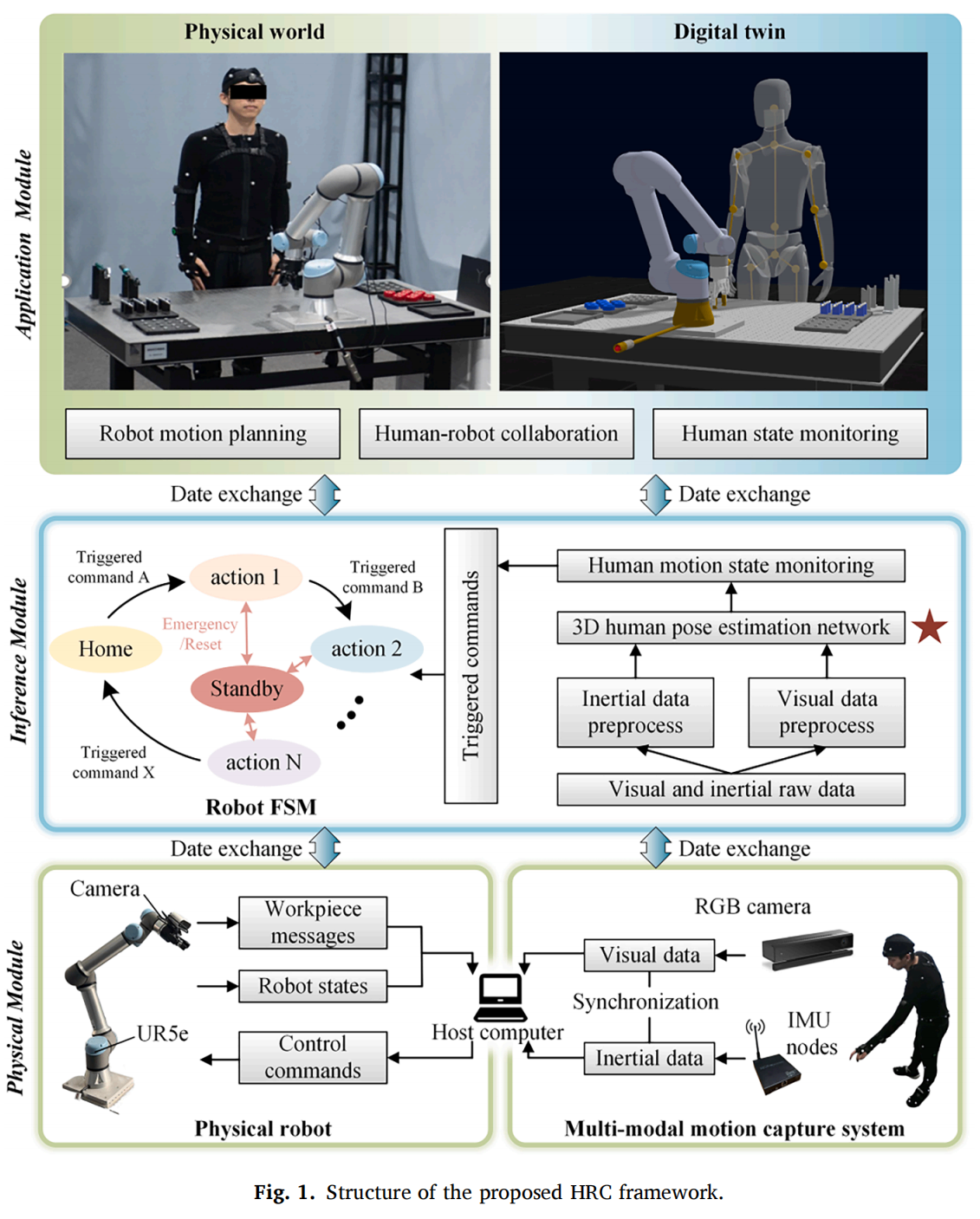
This research focuses on human-centric smart manufacturing scenarios, proposing a visual-inertial fusion-based method for human pose estimation to mitigate the impact of occlusions in industrial environments. NOKOV motion capture system provided ground-truth human pose data for the study, for the validation of the proposed method.
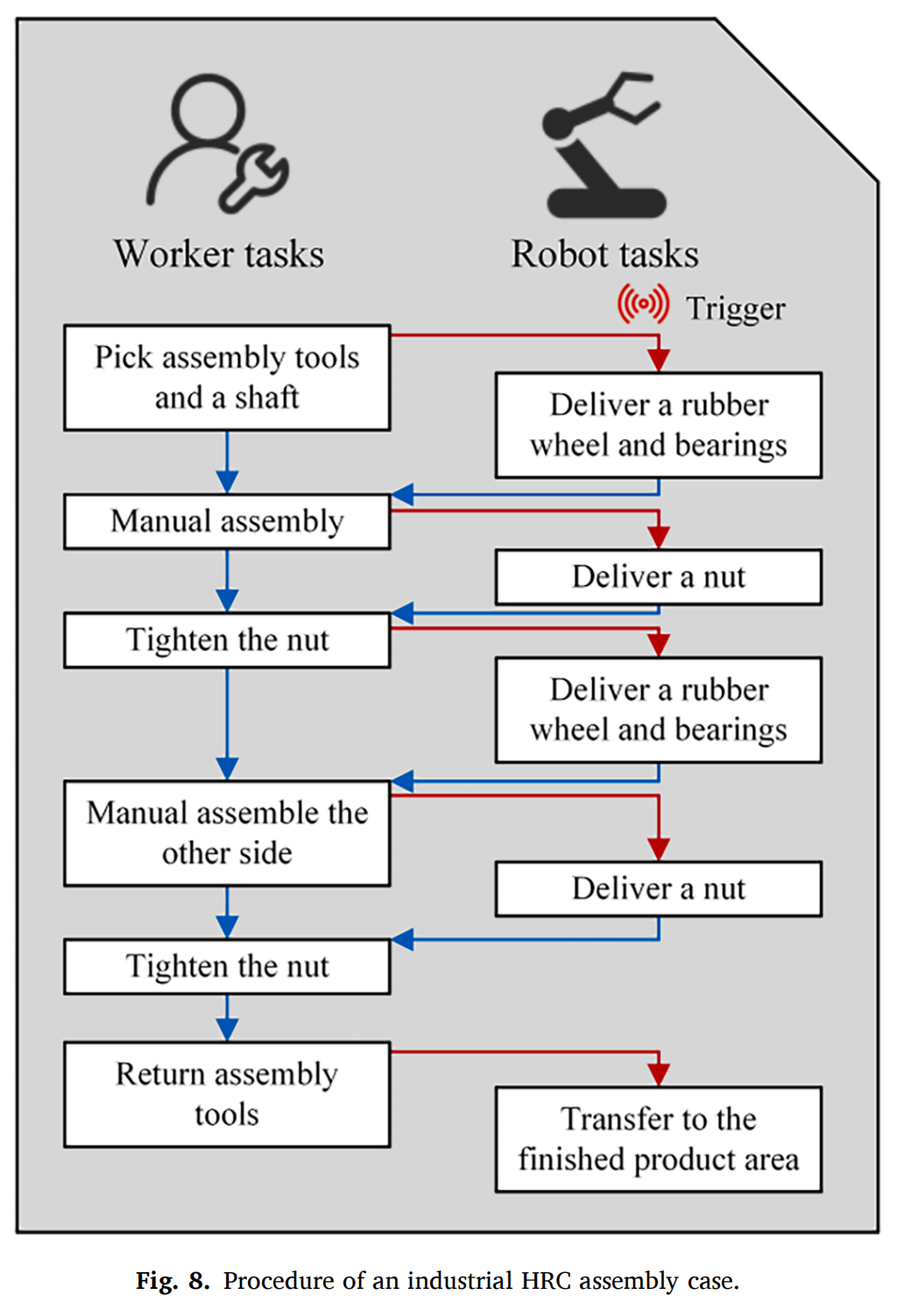
Compared to state-of-the-art methods, the proposed Human Pose Estimation (HPE) method demonstrates higher accuracy on both public and custom datasets and exhibits robustness in occluded scenarios. The contributions of this work are summarized as follows:
1. A novel visual-inertial fusion-based HPE method is developed for occluded Human-Robot Collaboration (HRC) scenarios. It utilizes a single RGB camera and sparse IMUs as inputs, balancing algorithmic performance and operator comfort.
2. A part-specific cross-modal transformer-based fusion block is designed to integrate spatial features from different modalities, facilitating effective data fusion.
3. a. Comprehensive experiments conducted on two public datasets and a synthetic-occlusion dataset demonstrate the competitive performance and occlusion robustness of the proposed method. b. An HPE dataset collected from an HRC assembly process, containing video, IMU data, and 3D ground truth annotations, is developed to validate the application performance.
This work validates the performance and robustness of the proposed visual-inertial fusion-based HPE method across various scenarios. During the construction of the custom dataset, the high-precision ground truth data provided by NOKOV optical motion capture system was utilized to assess the accuracy of the proposed method (Figs. 9, 10, 11).
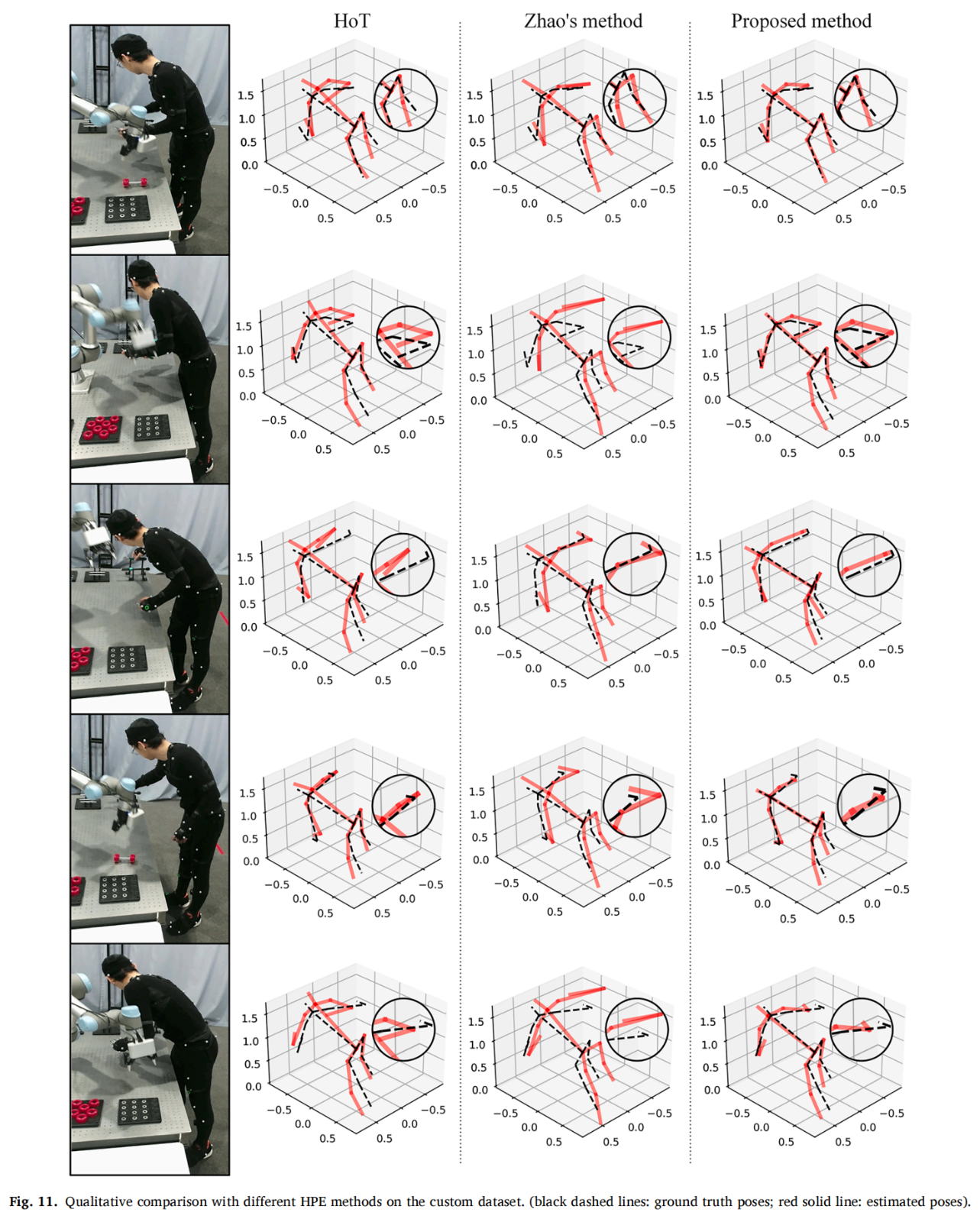
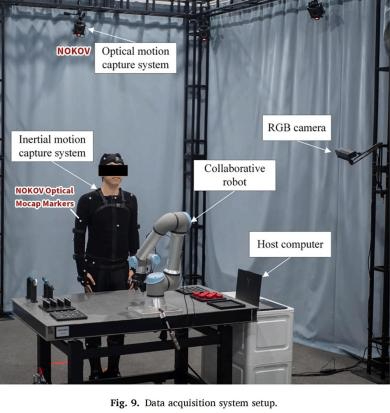
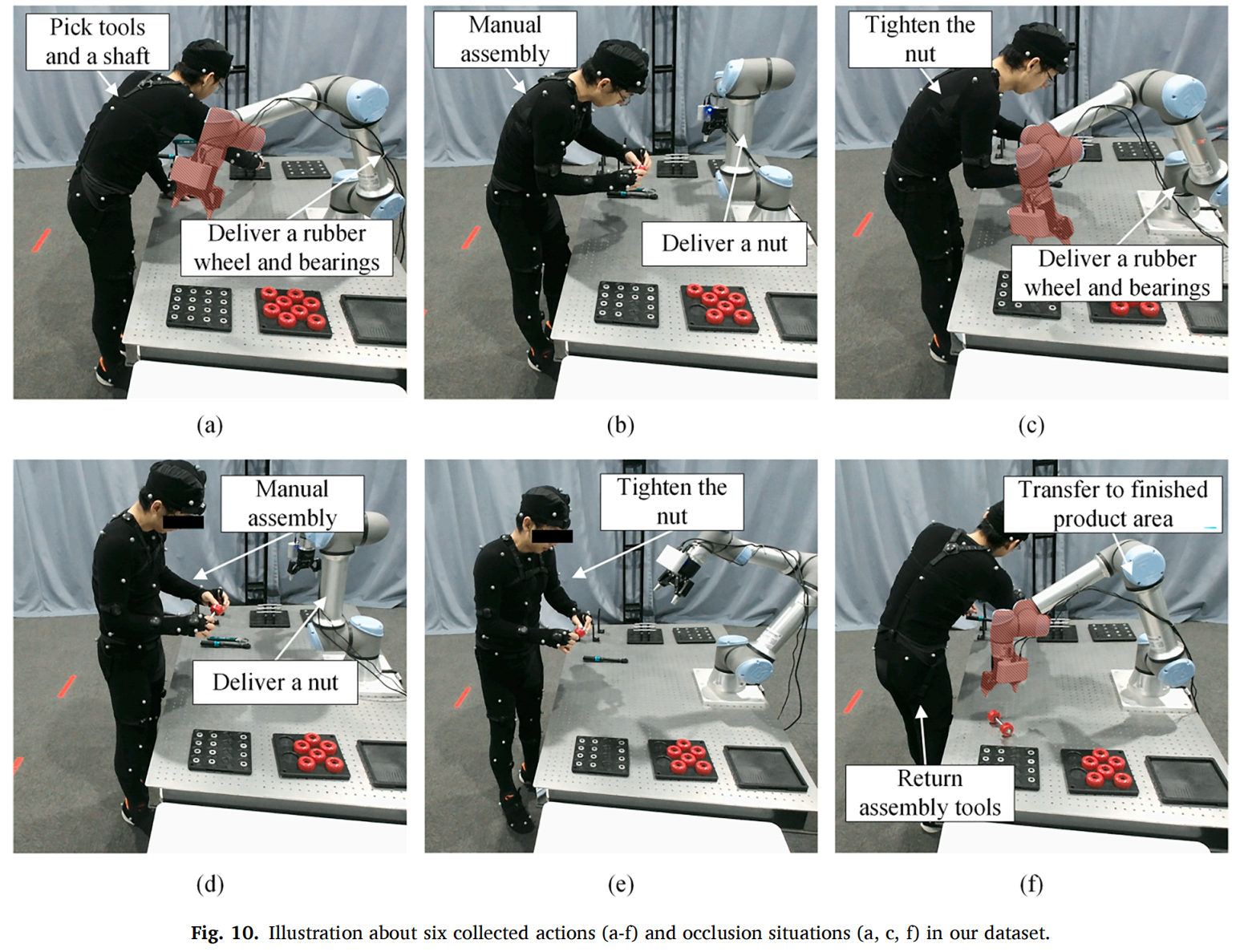

NOKOV motion capture system provides high-precision human pose ground truth, for the validation of the proposed method.
Authors’ Profile:
Baicun Wang (Corresponding Author): Associate Dean, Qiushi Distinguished Professor, Doctoral Supervisor, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University.
Ci Song: Ph.D. Candidate, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University.
Xingyu Li: Assistant Professor, School of Engineering Technology, Purdue University.
Huiying Zhou: Ph.D. Candidate, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University.
Huayong Yang: Academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE); Director of the Faculty of Engineering, Professor, Doctoral Supervisor, School of Mechanical Engineering, Zhejiang University.
Lihui Wang: Fellow of the Canadian Academy of Engineering (CAE); Professor and Head of Sustainable Production, Department of Production Engineering, KTH Royal Institute of Technology