A research team led by Professor Li Xiang from the Department of Automation at Tsinghua University has proposed a generative-model-based trajectory optimization framework for upper-limb exoskeleton robots. This framework is capable of generating highly individualized motion trajectories while ensuring safety, thereby providing personalized rehabilitation assistance training for stroke patients. The related research paper, "Upper-limb rehabilitation with a dual-mode individualized exoskeleton robot: A generative-model-based solution," has been published in the top-tier journal in robotics research, The International Journal of Robotics Research.
In the study, NOKOV Motion Capture System was used to precisely measure the joint angle data of the patient's healthy limb, which was utilized by the exoskeleton robot to adjust the reference trajectory for the affected side, thereby facilitating personalized rehabilitation training.
Citation
Chen Y, Miao S, Ye J, et al. Upper-limb rehabilitation with a dual-mode individualized exoskeleton robot: A generative-model-based solution. The International Journal of Robotics Research. 2025;0(0). doi:10.1177/02783649251333479
Background
Exoskeleton robots play a significant role in stroke rehabilitation. However, existing upper-limb exoskeleton robots are limited in terms of degrees of freedom (DoFs) and personalized assistance. They cannot fully match the movement range of a healthy person or adjust interaction forces based on the patient's real-time feedback, thereby limiting the quality and effectiveness of rehabilitation training. To overcome these limitations, the research team led by Professor Li Xiang developed a novel dual-mode individualized upper-limb exoskeleton robot, aiming to provide personalized stroke rehabilitation training support through its online generative capability.
Contributions
This paper introduces a generative-model-based dual-mode individualization framework. This framework comprises an intention predictor and an anomaly detector, designed to capture the motion intentions of the patient's unaffected side and to assess the safety and naturalness of human-robot interaction in real-time during rehabilitation tasks. In the active mirroring mode, the assistance reflects the patient's original motion intentions. In the passive following mode, the assistance is individualized based on interactive feedback.
Overall Structure
The overall architecture of the novel upper-limb exoskeleton robot includes its hardware design and software system. In terms of hardware, the robot features six degrees of freedom and employs series elastic actuators (SEAs) and a cable-driven mechanism to achieve compliant actuation and high safety. In terms of software, the robot adopts a hierarchical control architecture: the low level is responsible for motion control and environmental perception, while the high level runs on a personal computer, executing motion planning and computationally intensive tasks. All programs are integrated into the Robot Operating System (ROS).
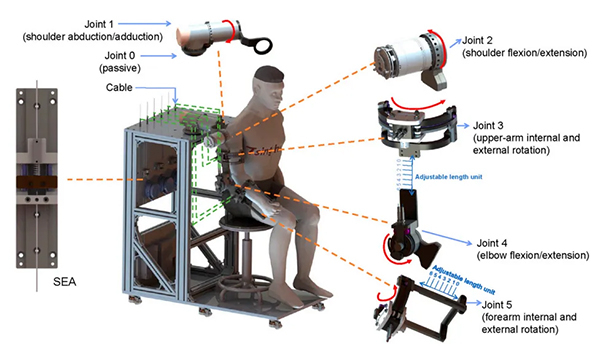
Figure 1 Overview of the developed upper-limb exoskeleton robot, which is cable-driven and consists of five active joints (Joints 1–5) and one passive joint (Joint 0).The red arrows indicate the directions of positive joint movements.
Experiments
1. Active Mirroring Training Experiments
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method in active mirroring training, experiments were conducted involving external impact tests, abnormal region identification tests, and overall motion tracking tests. During the experiments, NOKOV Motion Capture System was used to precisely measure the joint angle data of the patient's healthy limb, which the exoskeleton robot used to adjust the reference trajectory for the affected side.
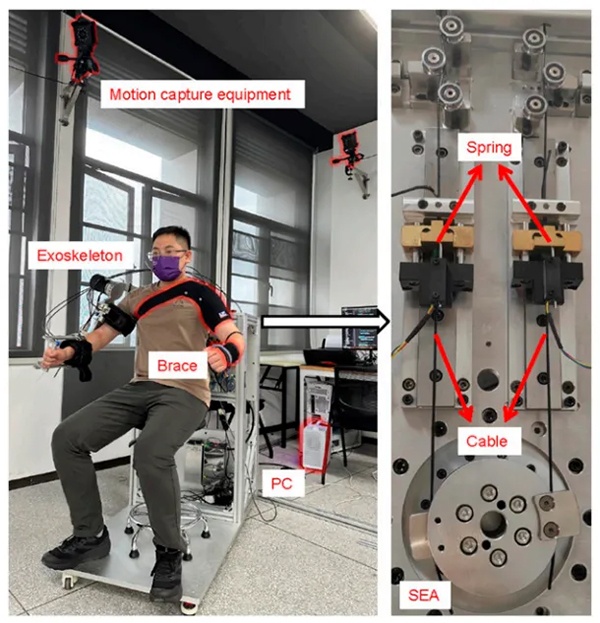
Figure 2 The experimental setup in active mirroring mode used motion capture equipment to obtain feedback from the unaffected side of the body. The SEA was constructed by connecting the motor output and the joint end with a spring and cable.
The experimental results show that the trajectory refinement is effective, meets the real-time requirements of rehabilitation training, and maintains good stability in human-robot interaction. The method can effectively track motion intentions, adapt to unexpected changes, and guide the robot towards safer regions.
Active mirroring training experiment
2. Passive Following Training Experiments
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed individualization framework in passive following training tasks, ablation studies, individualized assistance effectiveness evaluation, and a clinical trial were conducted. In the clinical trial results, the experimental group showed significant improvements in all evaluation metrics compared to their initial assessments, including reduced muscle tone levels and increased Fugl-Meyer Assessment (FMA) scores, indicating that passive following training accelerated the recovery of motor functions.
The experimental results demonstrate that the method proposed in this paper accelerated the recovery of motor functions, with significant improvements in both muscle tone levels and FMA scores.
Clinical experiment
NOKOV Motion Capture System provided high-precision limb joint angle data for the active mirroring training experiments in this study, which was used for the exoskeleton robot's reference trajectory, contributing to the validation of the effectiveness of the proposed method.
Authors’ Profile
Yu Chen, Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Ph.D. candidate. Main research interests: exoskeleton robots, human-robot interaction.
Shu Miao, Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Postdoctoral researcher. Main research interests: robot-assisted micromanipulation, medical robotics.
Jing Ye, Shenzhen MileBot Robotics Co., Ltd., Co-founder. Main research interests: exoskeleton robots, motion control, artificial intelligence.
Gong Chen, Shenzhen MileBot Robotics Co., Ltd., Co-founder. Main research interests: rehabilitation and assistive exoskeleton robots, human-robot interaction control, brain-computer interfaces.
Jianghua Cheng, Department of Rehabilitation, South China Hospital, Medical School, Shenzhen University, Head Therapist. Main research interests: innovative applications of rehabilitation therapy techniques.
Ketao Du, Department of Rehabilitation, South China Hospital, Medical School, Shenzhen University, Head of Department. Main research interests: innovative applications of rehabilitation therapy techniques.
Xiang Li (Corresponding Author), Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Associate Professor, Ph.D. supervisor. Main research interests: dexterous manipulation, human-robot interaction, medical robotics, micro-robotics.